



With the announcement this month from Microsoft that it has successfully fabricated its first quantum processor based on a novel material known as a ‘topological conductor’, the ID and secure document market faces a critical challenge: ensuring the security of cryptographic systems against potential quantum threats.
A recent survey on post-quantum cryptography (PQC) reveals insightful perspectives from industry professionals, highlighting both the readiness and the hurdles in adopting PQC solutions.
The survey, organised by Reconnaissance in cooperation with IDEMIA Smart Identity, was conducted between September and November 2024. A small number of selected PQC and cyber security professionals shared their views on the status of preparedness for the era of quantum computers in both private and public organisations.
The survey results indicate a strong awareness among respondents of the potential impact of quantum computing (QC) on current cryptographic systems.
Out of 35 respondents, 29 rated their understanding as ‘good’, ‘very good’, or ‘excellent’, while only six rated it as ‘fair’ or ‘poor’. This high level of awareness is crucial as it underscores the industry’s recognition of the impending quantum threat.
The belief in the emergence of QC is nearly unanimous among participants in the survey. Only four respondents expressed scepticism, stating that QC is ‘not very likely’ or that ‘I don’t think it will happen’.
The majority view underscores the urgency in preparing for a quantum-secure future, as most professionals anticipate QC becoming a reality within the next decade.
The survey highlights a strong consensus on the importance of implementing PQC within organisations.
15 respondents rated it as ‘very Important’, nine as ‘moderately’ or ‘slightly important’ and only one as ‘not at all important’. This recognition is a positive indicator that the industry is aware of the need to transition to quantum-resistant cryptographic solutions to safeguard sensitive personally identifiable information.
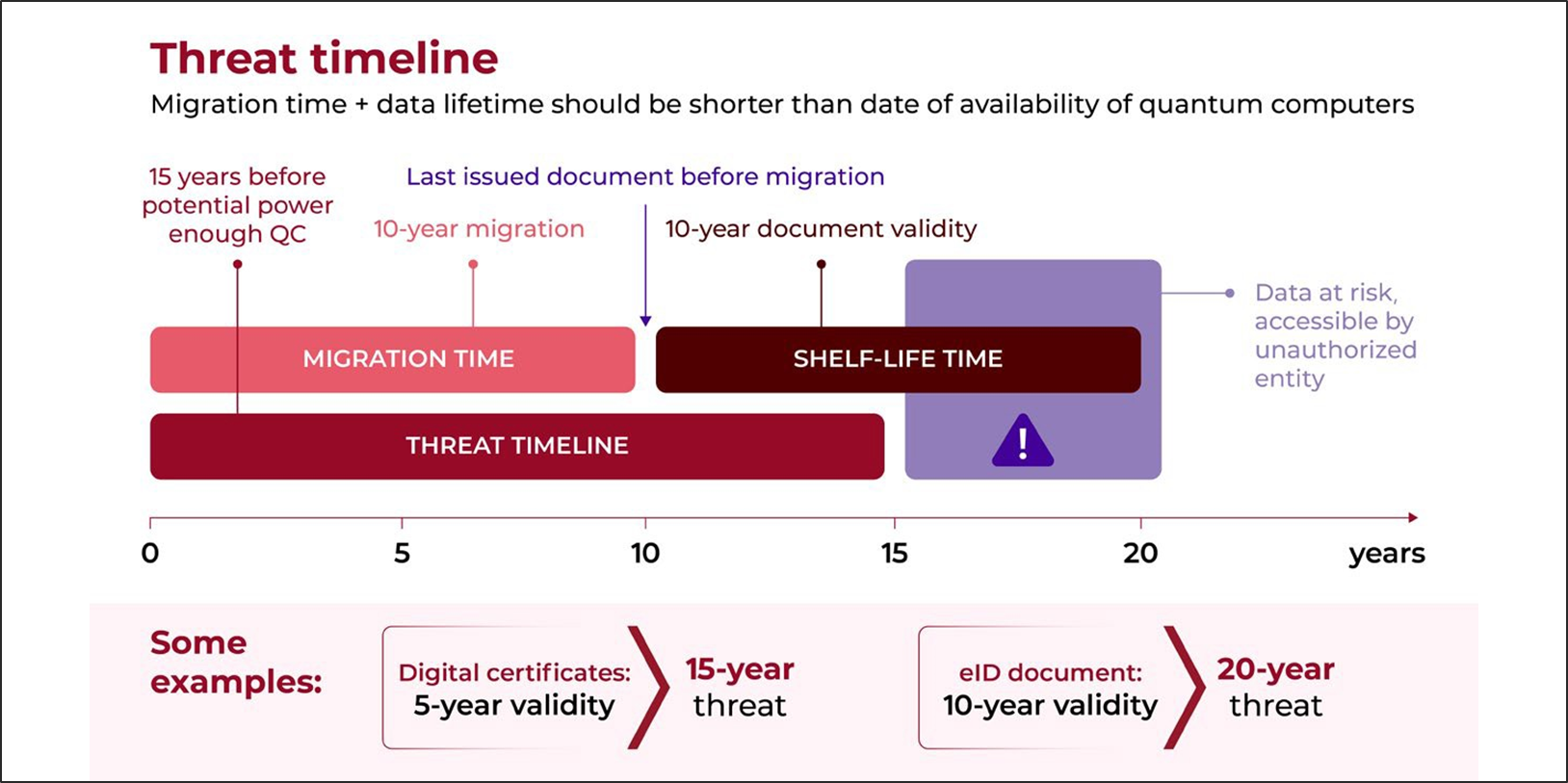
The ‘Threat timeline’ chart illustrates the urgency of transitioning to quantumresistant cryptographic systems before quantum computers break current encryption, as ‘store now, decrypt later’ threats put sensitive eID documents at risk due to their 10-year ‘shelf-life’.
Despite the awareness and recognition of the QC impact, significant barriers to PQC adoption remain. The primary challenges identified in the survey are the lack of knowledge and expertise, and the technical complexity of PQC technologies.
Many organisations lack the necessary know-how to implement PQC solutions effectively. Cybersecurity professionals, who are typically tasked with this responsibility, often do not have a background in quantum cryptography. The complexity of PQC technologies poses a significant hurdle, as organisations need to navigate the intricate technical landscape to develop and deploy quantumresistant solutions.
The ID and secure document industry is not alone in facing these challenges.
According to an article in Forbes, hundreds of companies are actively seeking skilled quantum workers. This demand highlights the broader industry trend and the need for specialised talent to drive PQC adoption.
Encouragingly, just over 50% of the survey respondents have either started implementing PQC solutions or are planning to do so. This proactive approach demonstrates a commitment to securing cryptographic systems against future quantum threats. However, these organisations are also seeking support and guidance to navigate the complexities of PQC adoption.
The survey respondents identified three key initiatives to facilitate PQC adoption: increased awareness, better education, and clarification on regulations and standards.
There is a clear need for educational initiatives to enhance understanding of PQC technologies and their implementation. In addition, clear and consistent regulations and standards are essential to guide organisations in developing their PQC strategies.
Within each organisation it will fall to the Information Security Office to become the key point of contact for support, providing the necessary expertise and resources to assist in the transition to PQC.
The road towards post-quantum cryptography is complex and challenging, but the survey showed that the ID and secure document market is making significant strides. With a strong understanding of the potential impact of QC, a conviction in its emergence, and a recognition of the importance of PQC, the industry is well-positioned to tackle the challenges ahead. By addressing the barriers of knowledge and technical complexity, and seeking support from key stakeholders, organisations can successfully navigate this transition.
‘When we discuss PQC-readiness with our clients, it becomes obvious that, although the topic is high up on the list of priorities, the professionals tasked simply don’t know where to start.
We see a respect towards the topic’s complexity that we can only solve by joining forces as an industry.
We won’t double the number of PQC-experts over night, but there are enough of us, to give the relevant advice at this point in time.’
Jerome Boudineau
PQC Expert at IDEMIA Smart Identity To find out more, visit Post-Quantum Cryptography in identity management – IDEMIA.
To find out more, visit Post-Quantum Cryptography in identity management – IDEMIA.